JS Array methods that programmers breathe
What's up? programmers! As you know, array methods are a very essential part of programming.
Javascript provides us with a wide variety of methods to perform various operations on an array.
Selecting and using the correct array method based on our needs can make a developer's life a lot easier and make the dev more productive.
So, let's start our journey with a brief overview of some must-know JS array methods.
1. filter
It creates a new array (shallow copy) from the given array by filtering down elements that pass test conditions implemented in the provided callback function.
array.filter((element, index, array) => { /* … */ } )Uses:
Example 1:
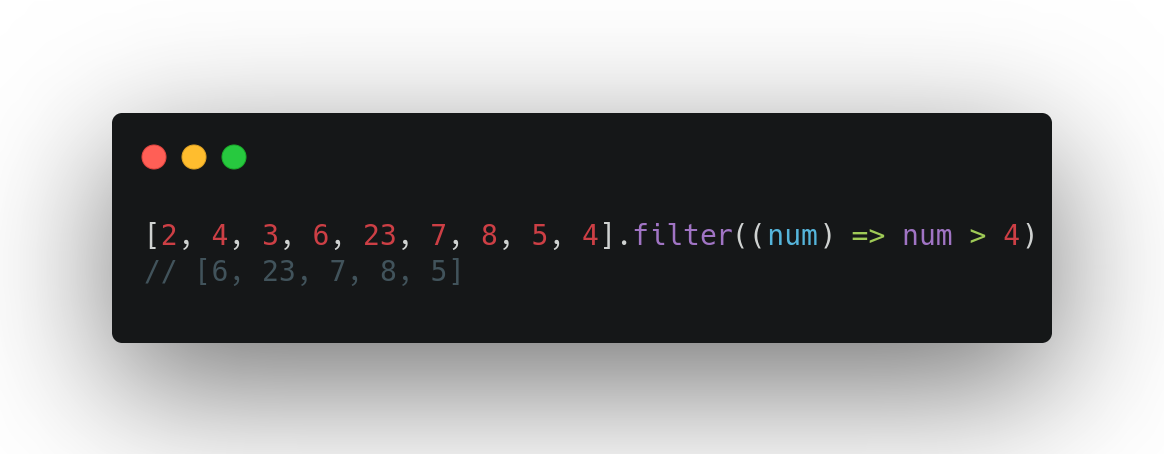
Example 2:
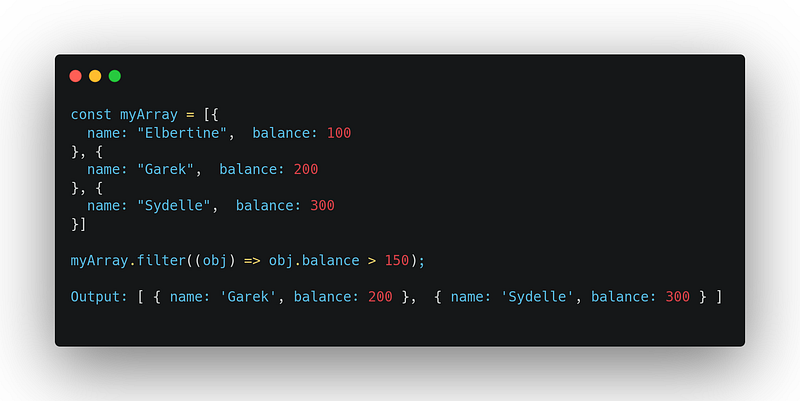
2. some
It returns true, if at least one element passes the test implemented in the given callback function, else returns false
array.some((element, index, array) => { /* … */ } )Uses:
Example 1:

Example 2:
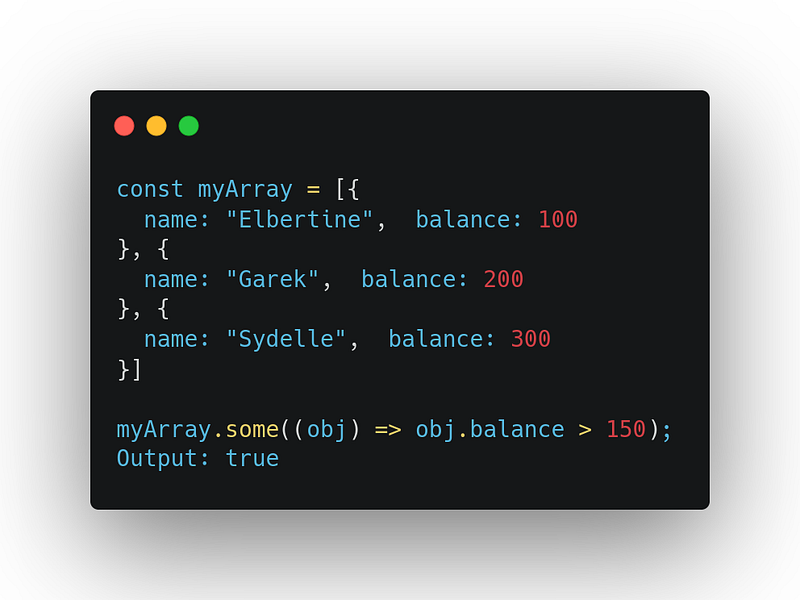
3. every
It returns true if, all the elements pass the test implemented by the provided callback function, Otherwise false
array.every((element, index, array) => { /* … */ } )Uses:
Example 1:

Example 2:
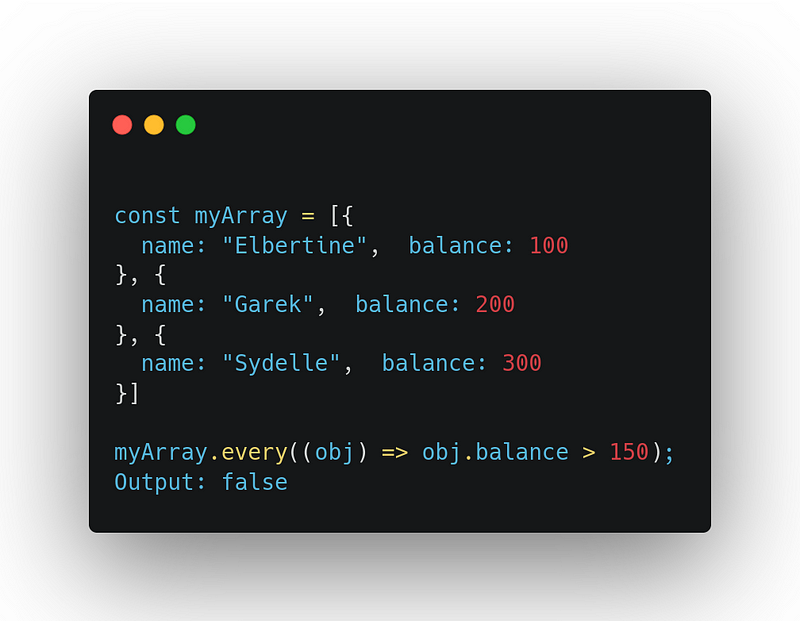
4. includes
It returns true if provided elements exist in the array, Otherwise false
array.includes(searchElement, fromIndex)Uses:

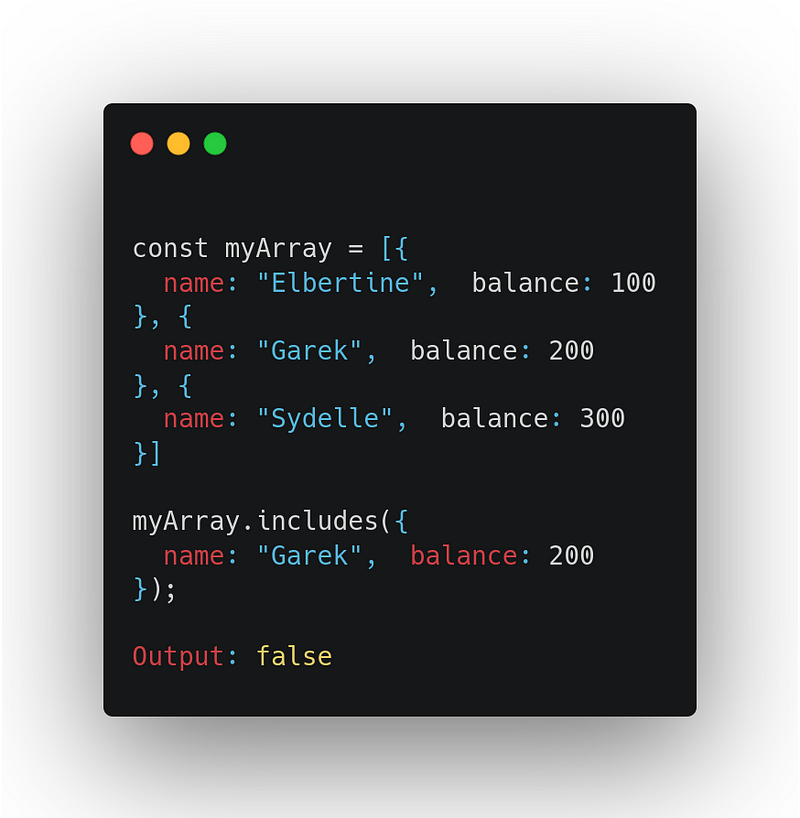
For Object, you should use find or another similar method for checking given object exists in the array or not
Reason: As the includes function compares objects by reference like obj1 === obj2,
As we pass an object as an argument in includes it passes a new object reference for comparison. Thus, even though the passed object contains values similar to one of the existing elements, but has a different reference, it causes a mismatch, and myArray.includes(obj) returns a false value.
see the following example.
5. map
It creates a new array after calling the given callback function for each element of the given array.
array.map((element, index, array) => { /* … */ })Uses:
Example 1:

Example 2:

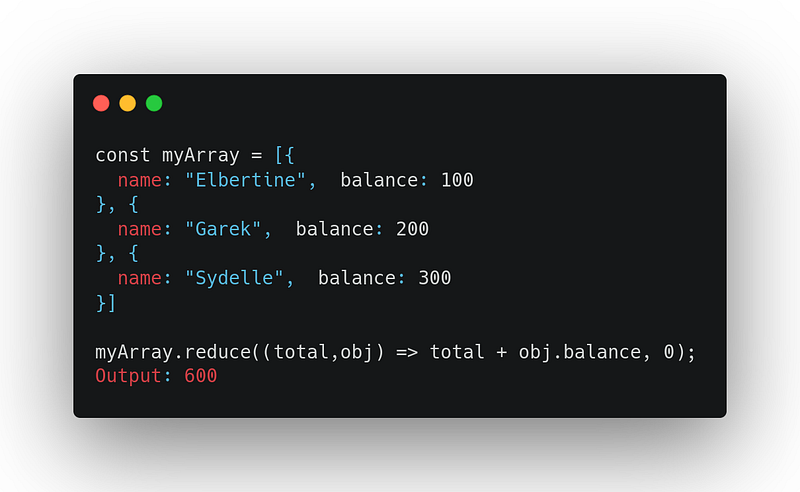
6. reduce
It executes provided reducer (callback) method for each element of the given array, in the same order and passes the return value of the previous function call, in the function call of the current element as the first argument for the reducer function.
- For the first reducer function call it will use the provided initial value (if provided)
- Otherwise, use the
1stelement as the initial value and start calling the reducer function with the2ndelement for the array
array.reduce((previousValue, currentValue, currentIndex, array) => { /* … */ }, initialValue)Uses:
Example 1:
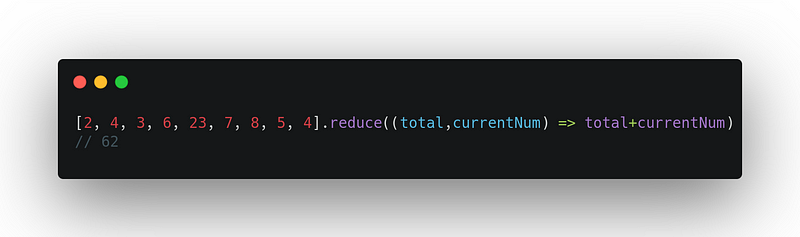
Example 2:
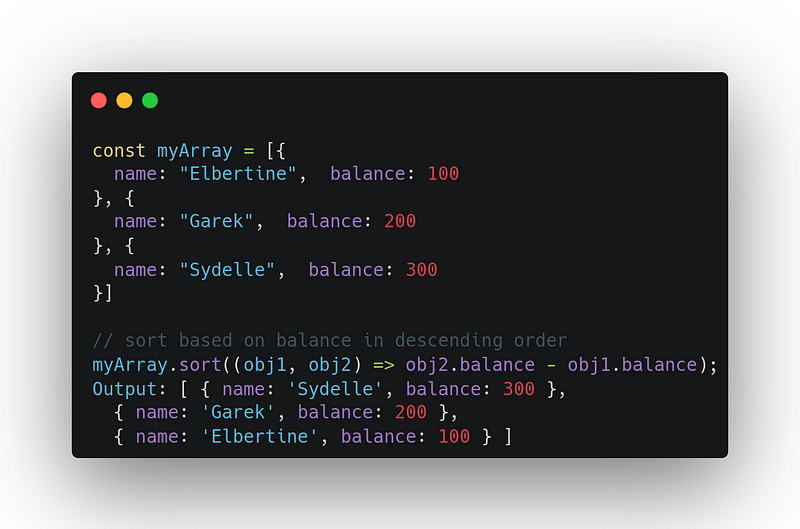
7. sort
It sorts array elements and returns the same array (with sorted elements)
- The default sort order is ascending.
- For comparison: it first converts elements into strings and then compares their sequences of UTF-16 code unit values.
array.sort((a, b) => { /* … */ } )Uses:
Example 1:

Example 2:
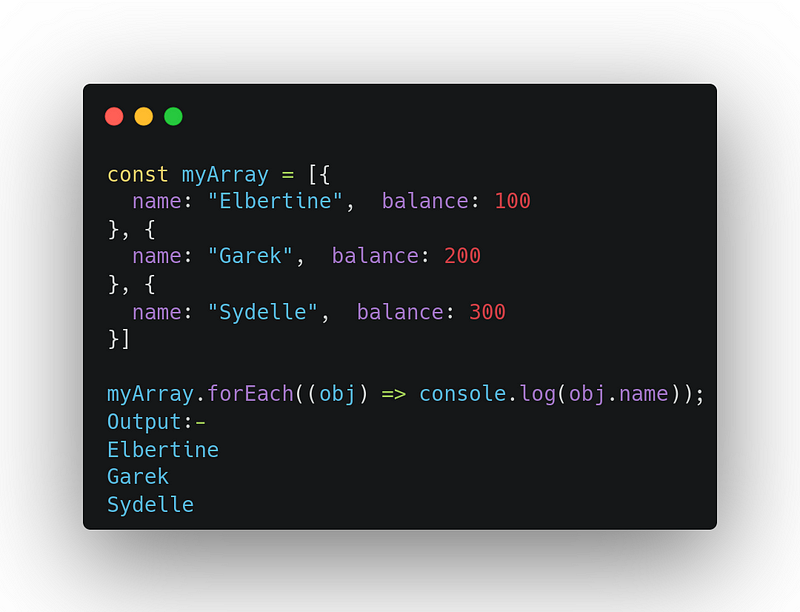
8. forEach
It executes the provided callback function for each element in the provided array.
array.forEach((element, index, array) => { /* … */ })Uses:
Example 1:

Example 2:
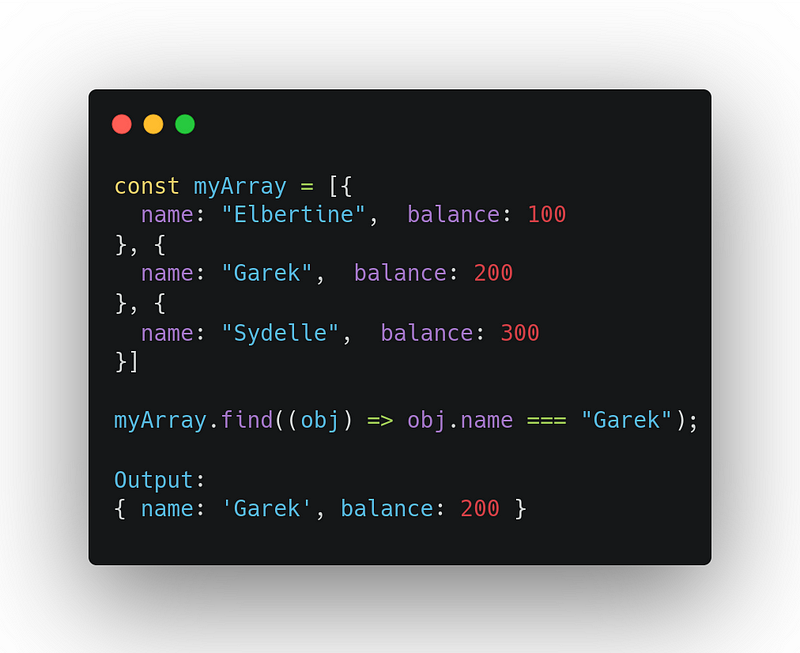
9. find
It returns the first element that passes the test in the provided callback function (test function). if none of the elements passes the test, it returns undefined
array.find((element, index, array) => { /* … */ } )Uses:
Example 1:

Example 2:
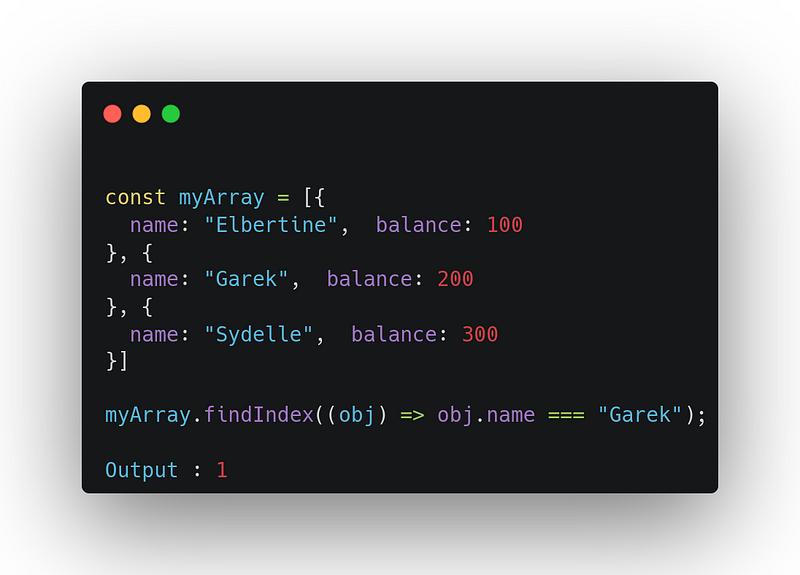
10. findIndex
It returns the index of the first element that passes the test in the provided callback function (test function). if none of the elements passes the test, it returns -1
array.findIndex((element, index, array) => { /* … */ } )Uses:
Example 1:

Example 2:
Conclusion
Here we discussed some of the essential JS array methods, their syntax, a normal example, and an example with an array of objects.
If you have reached so far in this journey. You have gained a lot. 🔥
Give a pat on your shoulder 😎
There are a lot of other important JS array methods, that are very useful in day-to-day programming.
Let us know in the comments, what other JS array method you know. 💡
Peace out!
You can check the full list of array methods here: https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Array